The Paradoxical Sleep by Relaxation Sleepy Time Ensemble on Statements

The Waking Nightmare of "Paradoxical Insomnia" - Pulse Nigeria Things To Know Before You Buy
Brain energy use in Rapid Eye Movement, as determined by oxygen and glucose metabolic process, equates to or exceeds energy use in waking. The rate in non-REM sleep is 1140% lower. Brain stem [modify] Neural activity throughout REM sleep appears to come from in the brain stem, particularly the pontine tegmentum and locus coeruleus. Rapid Eye Movement sleep is stressed and immediately preceded by PGO (ponto-geniculo-occipital) waves, bursts of electrical activity originating in the brain stem.
They display their greatest amplitude upon moving into the visual cortex and are a reason for the "quick eye motions" in paradoxical sleep. Other muscles might likewise contract under the influence of these waves. Forebrain [edit] Research in the 1990s utilizing positron emission tomography (FAMILY PET) verified the function of the brain stem and recommended that, within the forebrain, the limbic and paralimbic systems showed more activation than other areas.

PDF] Influence of paradoxical sleep deprivation and sleep recovery on testosterone level in rats of different ages- Semantic Scholar
The "anterior paralimbic REM activation location" (APRA) consists of locations linked with feeling, memory, worry and sex, and may therefore associate with the experience of dreaming during REMS. The Most Complete Run-Down has actually shown that the distribution of brain activity throughout Rapid Eye Movement sleep varies in correspondence with the type of activity seen in the previous period of wakefulness.
Paradoxical Sleep: Deprivation in the Cat - Science Can Be Fun For Everyone
The amygdala is likewise active during Rapid Eye Movement and might take part in generating the PGO waves, and experimental suppression of the amygdala results in less REM sleep. The amygdala may likewise control cardiac function in lieu of the less active insular cortex. Chemicals in the brain [edit] Compared to slow-wave sleep, both waking and paradoxical sleep involve higher use of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which might trigger the much faster brainwaves.
Injections of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, which successfully increases offered acetylcholine, have actually been found to cause paradoxical sleep in humans and other animals currently in slow-wave sleep. Carbachol, which mimics the result of acetylcholine on nerve cells, has a comparable influence. In waking human beings, the exact same injections produce paradoxical sleep just if the monoamine neurotransmitters have actually currently been diminished.
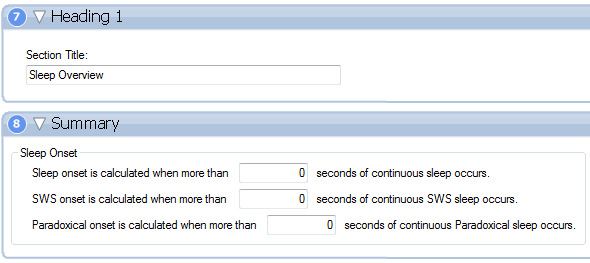
PLOS ONE: A Very Large Number of GABAergic Neurons Are Activated in the Tuberal Hypothalamus during Paradoxical (REM) Sleep Hypersomnia
Unlike the abrupt transitions in electrical patterns, the chemical modifications in the brain show continuous routine oscillation. Designs of REM regulation [modify] According to the activation-synthesis hypothesis proposed by Robert Mc, Carley and Allan Hobson in 19751977, control over Rapid Eye Movement involves paths of "REM-on" and "REM-off" nerve cells in the brain stem.

